Diesel Engines 101
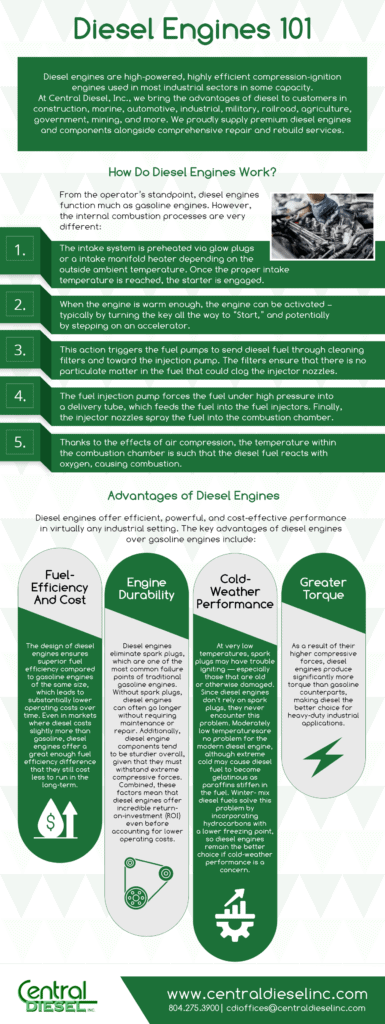
Leave a CommentDiesel engines are internal combustion engines that operate on the principle of compression ignition. Unlike gasoline engines, which rely on spark plugs for ignition, diesel engines use the heat generated by compressing air to ignite the fuel. They are known for their efficiency, durability, and high torque output, making them popular in various applications.
In this guide, we will take a closer look into the inner workings of diesel engines, uncovering their advantages and impact on various industries.
The Components of a Diesel Engine
To understand how diesel engines work, it is helpful to break down their key components:
- Cylinder block and pistons: The cylinder block houses the cylinders where combustion occurs. The pistons move up and down within these cylinders, compressing air and fuel and driving the crankshaft during the power stroke.
- Fuel injection system: Diesel engines use a fuel injection system to deliver precise amounts of diesel fuel into the combustion chamber at the right moment.
- Turbocharger: Many diesel engines are equipped with a turbocharger. It uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine that compresses incoming air before it enters the combustion chamber. This allows for more efficient combustion and increased power output.
- Cooling system: Diesel engines generate significant heat during operation, so an effective cooling system is essential to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance.
Benefits of Diesel Engines

Diesel engines offer several advantages over their gasoline counterparts, making them a preferred choice for various applications. Here are some of its key benefits:
Fuel Efficiency
Diesel engines are known for their superior fuel efficiency compared to gasoline engines. They typically consume less fuel to produce the same amount of power due to their higher compression ratios and better thermal efficiency. This results in lower fuel costs, especially in vehicles and equipment with high fuel consumption rates, such as trucks and heavy machinery.
Durability and Longevity
This engine type is renowned for its robust construction and longevity. It is built to withstand higher stress levels and compression, making it more durable and reliable over extended periods of use. This translates to lower maintenance costs and longer service intervals, contributing to overall cost savings.
Power
Diesel engines produce more power per unit of displacement compared to gasoline engines. They can achieve higher power outputs with smaller engine sizes, resulting in more compact and lightweight designs without compromising performance. This is particularly advantageous in applications with limited space and weight, such as marine vessels and heavy machinery.
Low Carbon Dioxide Emissions
These engines emit less carbon dioxide (CO2) per mile due to their superior fuel efficiency. This makes them a more environmentally friendly option regarding greenhouse gas emissions, especially in vehicles that cover long distances or operate for extended periods.
Adaptability and Versatility
Various fuels are compatible with diesel engines, including biodiesel and synthetic diesel blends. They can also use renewable diesel from vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste materials. This allows for greater flexibility in fuel sourcing and promotes sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Reliability in Extreme Conditions
Diesel engines are well-suited for operation in extreme weather conditions, including cold temperatures, high altitudes, and rugged terrain. They offer better cold-start performance and maintain consistent power output even under challenging circumstances.
Applications of Diesel Engines
Diesel engines find applications across various industries and sectors, including:
- Transportation: heavy-duty trucks, freight, passenger rail transport, and buses
- Maritime: cargo ships, cruise liners, ferries, and tugboats
- Construction: excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and dump trucks
- Mining: haul trucks, drills, and loaders
- Agriculture: tractors, combine harvesters, and irrigation pumps
- Military: tanks, armored personnel carriers, and utility vehicles
- Power generation: standby generators and backup power sources for critical facilities such as hospitals, data centers, telecommunications infrastructure, and manufacturing plants
Central Diesel: Your Trusted Partner in Delivering Reliable Diesel Solutions

With over five decades of industry experience, Central Diesel is the trusted partner for thousands of customers looking to fulfill their diesel engine needs! We provide a comprehensive solution including installation, maintenance, and repair services ensuring your diesel engines operate at peak performance. Our extensive inventory includes components essential for replacements, repairs, and upgrades, such as filtration systems, fuel injection components, electrical parts, and turbocharger assemblies.
Contact us today to learn more about our services! You can also request a quote to get started.